Summary about Geomatics Engneering
Introduction
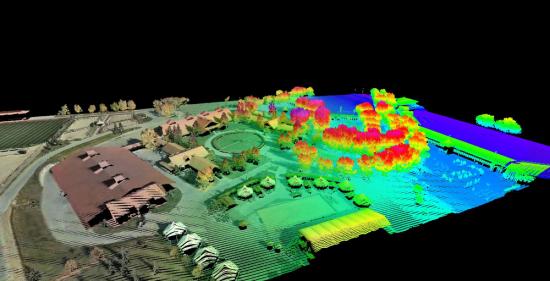
Geomatics Engineering, also called Geospatial Engineering is a rapidly developing discipline that focuses on spatial information. Geomatics engineers apply engineering principles to spatial information and implement relational data and manage local, regional, national and global spatial data infrastructures.Geomatics engineers design, develop, and operate systems for collecting and analyzing spatial information about the land, the oceans, natural resources, and manmade features. Geomatics engineering applications include integrating science and technology from both new and traditional disciplinesof science and engineering. Geomatics engineers utilize a wide range of technologically advanced tools such as digital theodolite/distance meter total stations, Global Positioning System (GPS) equipment, digital aerial imagery (both satellite and air-borne), and computer-based geographic information systems (GIS).
The fact that so few people have heard of geomatics has its Advantages: Graduates, whatever their level of qualification, will usually find a job as soon as they start looking. So, what sort of jobs can you expect to find?
The geomatics industry is diverse and crying out for recruits--it is in the unusual position of having more jobs than graduates. Geomaticians are equally likely to be found working for offshore companies positioning oil rigs and monitoring pipelines across oceans as they are to be found mapping utilities for your local council. Local authorities are always looking for people with GIS experience, as are utility and transport companies, supermarkets, and numerous other industries which you may not immediately associate with geomatics.
Experience and expertise in remote sensing (processing and analysing satellite images) or photogrammetry (making spatial measurements from photographs) may lead to rewarding jobs in environmental and national heritage organisations, or a career in the oil and minerals industry. Geomatics graduates certainly have extensive opportunities to travel, and usually with someone else paying the bills!
And then, there are research and academic opportunities too, if a career in this area appeals.
Key Skills for geomatics surveyors and land surveyors
**Numeracy and the ability to make mathematical calculations
**The ability to understand and interpret data
**Lateral and logical thinking
Cutting-edge IT skills and confidence with new technology
**Problem solving and analysis
Attention to detail
**Client management/customer service skills
**Verbal and written communication skills
**Organisation and time management
**The ability to work independently and as part of a team
Also: employers often require you to have a full driving licence in order to travel to sites.
The graduates of the Geomatics Engineering (GME) program should demonstrate competency in one or more of the following GME competency areas:
-Boundary/land surveying, photogrammetry, geodesy, GIS, and digital mapping.
A continued capacity for Employment in one or more GME specialty area.
A capacity for graduate education.
-Continued membership in professional organizations.
-A continuing commitment to lifelong learning.
-A continuing commitment to serving and protecting the health and welfare of the public.
-An ability to pass professional licensing or certification examinations after achieving requisite professional experience.
Job opportunities in Nepal
-Department of Survey and other governmental agencies involved in land management and infrastructure development
-Urban planners
-NGOs, INGOs
Sources:
http://www.wrc.edu.np/civil-geomatics-engineering/geomatics-engineering/
https://www.fresnostate.edu/engineering/civil-geomatics/geomatics/
http://www.sciencemag.org/careers/2003/05/geo-what-opportunities-geomatics
https://targetjobs.co.uk/careers-advice/job-descriptions/279587-geomaticsland-surveyor-job-description etc
Geomatics Engineering, also called Geospatial Engineering is a rapidly developing discipline that focuses on spatial information. Geomatics engineers apply engineering principles to spatial information and implement relational data and manage local, regional, national and global spatial data infrastructures.Geomatics engineers design, develop, and operate systems for collecting and analyzing spatial information about the land, the oceans, natural resources, and manmade features. Geomatics engineering applications include integrating science and technology from both new and traditional disciplinesof science and engineering. Geomatics engineers utilize a wide range of technologically advanced tools such as digital theodolite/distance meter total stations, Global Positioning System (GPS) equipment, digital aerial imagery (both satellite and air-borne), and computer-based geographic information systems (GIS).
The fact that so few people have heard of geomatics has its Advantages: Graduates, whatever their level of qualification, will usually find a job as soon as they start looking. So, what sort of jobs can you expect to find?
The geomatics industry is diverse and crying out for recruits--it is in the unusual position of having more jobs than graduates. Geomaticians are equally likely to be found working for offshore companies positioning oil rigs and monitoring pipelines across oceans as they are to be found mapping utilities for your local council. Local authorities are always looking for people with GIS experience, as are utility and transport companies, supermarkets, and numerous other industries which you may not immediately associate with geomatics.
Experience and expertise in remote sensing (processing and analysing satellite images) or photogrammetry (making spatial measurements from photographs) may lead to rewarding jobs in environmental and national heritage organisations, or a career in the oil and minerals industry. Geomatics graduates certainly have extensive opportunities to travel, and usually with someone else paying the bills!
And then, there are research and academic opportunities too, if a career in this area appeals.
Key Skills for geomatics surveyors and land surveyors
**Numeracy and the ability to make mathematical calculations
**The ability to understand and interpret data
**Lateral and logical thinking
Cutting-edge IT skills and confidence with new technology
**Problem solving and analysis
Attention to detail
**Client management/customer service skills
**Verbal and written communication skills
**Organisation and time management
**The ability to work independently and as part of a team
Also: employers often require you to have a full driving licence in order to travel to sites.
The graduates of the Geomatics Engineering (GME) program should demonstrate competency in one or more of the following GME competency areas:
-Boundary/land surveying, photogrammetry, geodesy, GIS, and digital mapping.
A continued capacity for Employment in one or more GME specialty area.
A capacity for graduate education.
-Continued membership in professional organizations.
-A continuing commitment to lifelong learning.
-A continuing commitment to serving and protecting the health and welfare of the public.
-An ability to pass professional licensing or certification examinations after achieving requisite professional experience.
Job opportunities in Nepal
-Department of Survey and other governmental agencies involved in land management and infrastructure development
-Urban planners
-NGOs, INGOs
Sources:
http://www.wrc.edu.np/civil-geomatics-engineering/geomatics-engineering/
https://www.fresnostate.edu/engineering/civil-geomatics/geomatics/
http://www.sciencemag.org/careers/2003/05/geo-what-opportunities-geomatics
https://targetjobs.co.uk/careers-advice/job-descriptions/279587-geomaticsland-surveyor-job-description etc





Comments
Post a Comment